Setup
Now it's time to set up: first, we'll test the camera, then we'll load and convert the AI model.
Camera Test
Accessing the camera is extremely easy; OpenCV provides easy-to-use methods for this purpose. The only important thing is to find out the camera number: the “VideoCapture” method requires the index of the camera to be used. Normally, every built-in camera (in a laptop or tablet) has the index 0, while an external camera (e.g., USB camera) has the index 1.
import cv2
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Open the video stream
cam = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
# Loop through the video frames
while cam.isOpened():
# Read a frame from the video
success, frame = cam.read()
if success:
# Display the annotated frame
cv2.imshow("TEST", frame)
# Break the loop if 'q' is pressed
if cv2.waitKey(1) == ord("q"):
break
else:
# Break the loop if the end of the video is reached
break
# Release the video capture object and close the display window
cam.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows
First YOLO Test
This is the standard test for YOLO: You load the "bus image" from the Ultralytics website and let YOLO recognize the existing objects:
from ultralytics import YOLO
# Load the pretrained model
model = YOLO("yolo11n.pt")
# recognition of the objects
results = model("https://ultralytics.com/images/bus.jpg")
# Visualize the results
for result in results:
result.show()
The result should look like this:
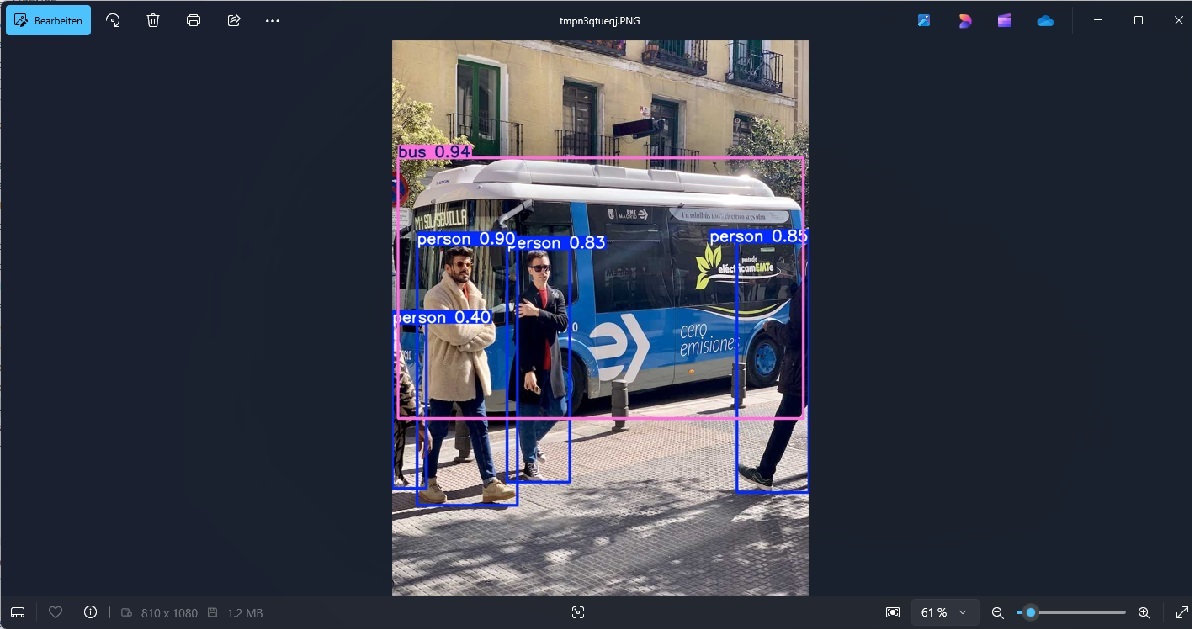
Conversion To NCNN
NCNN is a highly efficient inference framework optimized for mobile and embedded devices. When combined with YOLO (You Only Look Once), it offers several advantages: The combination with NCNN enables YOLO models to run in real-time on mobile devices without relying on high-performance GPUs. NCNN is platform-independent and does not require special runtime dependencies like CUDA. This makes deploying YOLO on devices without GPUs or specialized hardware more straightforward.
# Load a YOLO11n PyTorch model
model = YOLO("yolo11n.pt")
# Export the model to NCNN format
model.export(format="ncnn") # creates 'yolo11n_ncnn_model'
# Load the exported NCNN model
ncnn_model = YOLO("yolo11n_ncnn_model")
PyQt5 GUI API
The setup is now almost complete. We just need an API for programming the user interface, for which we will use PyQT5. PyQt5, a set of Python bindings for the versatile Qt application framework, has emerged as a powerful tool for developers seeking to craft cross-platform applications with ease and elegance. Combining Python's simplicity with Qt's comprehensive features, PyQt5 offers a seamless way to build engaging user interfaces.
The GPL version of PyQt5 can be installed from PyPI:
pip install PyQt5